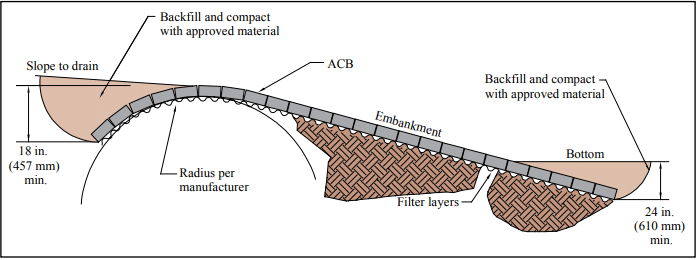
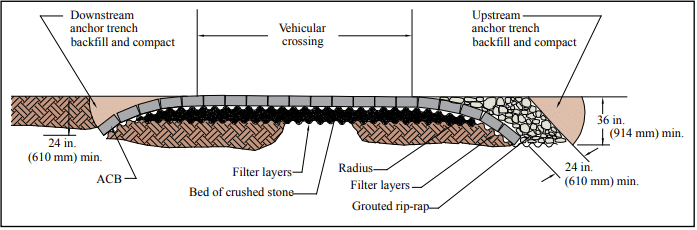
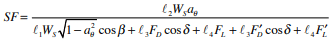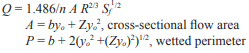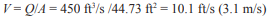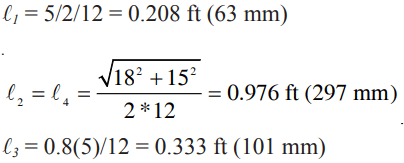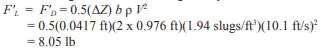ACB Revetment Design— Factor of Safety Method
INTRODUCTION
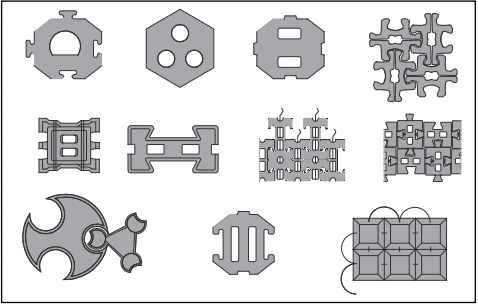
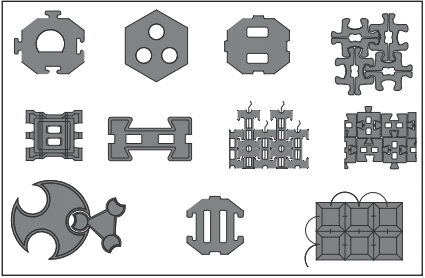
This Tech Note is intended to help designers understand the ACB design methodology and the different variables influencing the design and safety factor selection. Articulating concrete block (ACB) systems provide erosion protection to soil exposed to the hydraulic forces of moving water. ACB systems are a matrix of individual concrete blocks placed closely together to form an erosion-resistant overlay with specific hydraulic performance characteristics. Because it is composed of individual units, the ACB system can conform to minor changes in the subgrade without loss of intimate contact. Systems may be connected through geometric interlock and/or other components such as cables. Systems with openings in the blocks can typically be vegetated to provide a “green” channel and facilitate infiltration/exfiltration of channel moisture. Figure 1 illustrates a variety of ACB systems, but is not all-inclusive of available systems.
ACB units are concrete block produced in accordance with Standard Specification for Materials and Manufacture of Articulating Concrete Block (ACB) Revetment Systems, ASTM D6684 (ref. 1). Units must conform to minimum compressive strength, absorption and geometric specifications tested in accordance with Standard Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Concrete Masonry Units and Related Units, ASTM C140 (ref. 2).
This Tech Note addresses the structural stability of ACB revetment systems as a function of site-specific hydraulic conditions and unit characteristics. This Tech Note does not address geotextile filter and/or subgrade filter design, minimum installation guidelines critical to the proper performance of ACB revetments, or minimum upstream or downstream toe treatments. These topics are covered in design manuals such as references 5 and 6.
FACTOR OF SAFETY METHOD
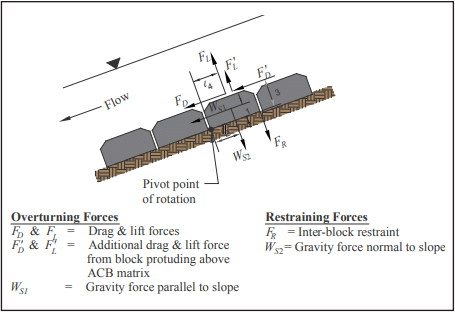
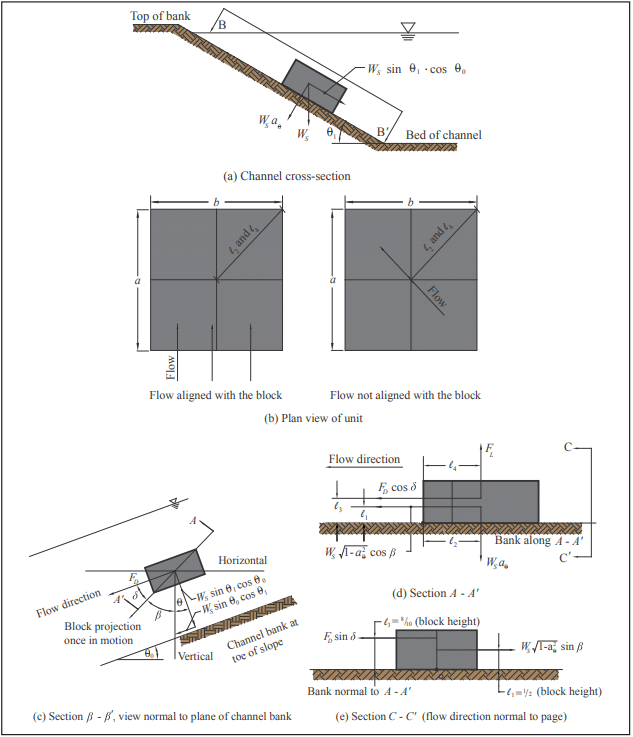
Similar to many rip rap sizing methods, the Factor of Safety method quantifies hydraulic stability of ACB systems using a “discrete particle” approach (see ref. 7). The design method involves balancing the driving and resisting forces, including gravity, drag and lift as illustrated in Figure 2. In typical channel and spillway applications, failure due to sliding (slipping) of the ACB revetment along the bed is remote. The revetment system is more apt to fail as a result of overturning about the downstream edge of the ACB unit, or downstream corner point when the ACB unit is located on the side slope of a steep channel. For cases where the revetment is placed on steep side slopes (2H:1V or steeper), the design should evaluate the potential for slip shear failures along geosynthetic-ACB unit interfaces induced by hydraulic and gravitational forces (i.e., potential slope instability).
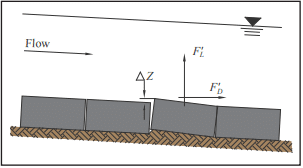
Fundamental principles of open channel flow and rigid body mechanics are used along with hydraulic test results supplied by manufacturers. The size and weight of the ACB units, as well as performance data from full-scale laboratory testing, are considered in evaluating the ratio of resisting to overturning moments (the “force balance” approach). This ratio defines the factor of safety against uplift. The design procedure accounts for additional forces applied to the unit when protrusions above the matrix occur, such as subgrade irregularities or due to improper placement (see Figure 3). Failure is defined as loss of intimate contact between the ACB unit and subgrade. The effects of cables or rods, vegetative root anchorage or mechanical anchorage devices are conservatively ignored.
Target Factor of Safety
There are several factors that need to be understood and considered when evaluating the appropriate target safety factor for design purposes. These can be categorized into two groups; external and internal factors. The external group consists of factors such as the complexity of the hydraulic system, the uncertainty of the input hydraulics, and the overall consequence of failure. These uncertainties are accounted for in the design by incorporating them into the target safety factor.
As discussed below, there are multiple facets of the safety factor methodology that are considered as they relate to external and internal design factors.
External Factors
- Complexity of the hydraulic system and uncertainty of the input hydraulics.
All hydraulic systems are not of the same complexity. Modeling the flow characteristics of a stream bank or channel is much different than the design of scour protection around bridge piers. If the flow is relatively uniform and predictable, then the designer may select a lower value for the target safety factor. As the complexity of the system increases, so too should the sophistication of the model used to determine the hydraulic parameters. Utilizing a simplistic model in a complex environment may warrant an increase in the target safety factor (i.e., greater than 1.5). Conversely, if a complex model is used to analyze a simplistic design scenario, then a lower target safety factor may be adequate (i.e., less than 1.5). - Consequence of failure.
As with the complexity of the hydraulic system, the overall consequence of failure needs to be understood. Failure that results in loss of life is much different from a failure resulting in soil erosion along a stream bank in which no loss of life or property is imminent. Increasing the target safety factor is one way of potentially offsetting environmental conditions that are considered high risk.
Internal Factors
- Extrapolation of Test Data.
In order to use the safety factor methodology, the critical shear stress of the unit along a horizontal surface must be understood and quantified. An equation is used for the extrapolation of test results from a steeper bed slope to a horizontal slope. A second extrapolation takes place from the tested units to thicker, untested units. In both processes, it is assumed that the intra-block restraint is the same for all thicknesses of the units. Under this assumption, the extrapolation equations only consider the weight and thickness of the units. This moment balance approach (obtained from the geometry of the unit) neglects any intra-block restraint. This assumption can be very conservative given the fact that thicker units have much more intra-block friction than thinner units given the shape of the blocks. As illustrated in Figure 4, the bottom half of an ACB unit is essentially a rectangle of concrete with adjacent units resting against six surrounding units (because the units are placed in a running bond pattern, there are six adjacent units, rather than four). As the unit increases in thickness, so too does the intra-block friction. Currently, the safety factor methodology does not account for this variable, which only increases the conservatism of this design approach for such conditions. - Performance Values.
Hydraulic testing on different “footprint” or classes of blocks and tapers for a variety of dam overtopping and spillway applications has been performed by system manufacturers. In many of these tests, the testing facility was unable to fail the system under a 4 ft (1.2 m) and 5 ft (1.5 m) overtopping scenario. Nevertheless, the resulting shear stresses obtained from the tests are used within the safety factor methodology as a threshold, or failure, shear stress. This issue is compounded when extrapolating to thicker units. Without being able to reach a threshold condition in the testing flume, licensors and manufacturers extrapolate shear stress value from a stable value. A large degree of conservatism in the performance values of the units is the result of not being able to fail these systems under laboratory conditions. - Interaction between Velocity and Shear Stress.
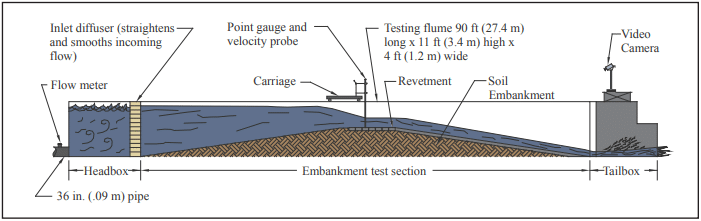
In flume testing of the units (see Fig. 5), two of the most important results obtained are: a stable shear stress; and, velocity at a downstream point under the highest flow conditions.Consider for example testing results whereby the highest boundary shear stress and velocity obtained was 22.2 lb/ft² (1,063 Pa) and 26.1 ft/s (7.96 m/s), respectively. In the safety factor methodology one utilizes a shear stress of 22.2 lb/ft² (1,063 Pa) regardless of the expected design velocity for every design utilizing this particular unit (provided that the design velocity is less than or equal to the tested velocity). Common “hydraulic” sense would state that if the velocity was only 12 ft/s (3.66 m/s) for a given application, then the system could withstand a much larger shear stress than 22.2 lb/ft² (1,063 Pa). Therefore, an additional degree of conservatism is present when the design velocity is less than the tested velocity and the design utilizes the maximum shear stress generated during the higher velocity event. - Allowable shear stress in a vegetated state.
All of the testing on existing ACB systems has taken place in a non-vegetated state. In contrast, many ACB applications for overtopping and spillway applications seek a final system that is fully vegetated. A series of hydraulic tests conducted by the U.S. Army Corp of Engineers investigated the performance of identical ACB systems in both vegetated and non-vegetated conditions (ref. 14). The end result was an increase in the allowable shear stress of 41% when vegetated.
Taking into consideration all of the points addressed above, what is the proper target safety factor required for a dam overtopping or spillway application? It is safe to state that the methodology used for ACB design is full of conservative assumptions. From the fact that tapered ACB systems have not reached their threshold condition in the testing flume to the fact that vegetation increases the allowable shear stress, it is apparent that the resulting safety factor can be conservative by 20 – 50%. Therefore, a target safety factor of 1.3 – 1.5 is adequate for applications in which the design hydraulics and site geometry are clearly understood, such as dam overtopping or spillway applications. Ultimately, the “external” factors and overall design of the project will need to be evaluated and decided on by the engineer of record. It may also be appropriate for an individual experienced in ACB design to offer an opinion on how these factors should be incorporated into an overall target safety factor.
Hydraulic Considerations
The main hydraulic variable in ACB stability design is the total hydraulic load (or bed shear stress) created by a varying discharge within a fixed geometric cross-section. The ratio of designed average cross-sectional bed shear to the ACB’s critical shear value (obtained from testing) is used, in part, for practical analysis and evaluation of ACB stability. The cross-section averaged bed shear stress, τo, can be calculated for design using a simple equation (ref. 13):
τo = γ R Sf
τo is applied over the channel boundary, regardless of o channel lining. Shear stress is a function of the hydraulic radius and the slope of the energy line (for the simplest case—the bed slope), both defined by channel geometry and flow conditions.
The cross-section averaged bed shear stress is suitable for uniform flow conditions such as those found in long straight reaches of open channels with uniform cross section. It may be determined using simplified model approaches, such as the Manning equation or the HEC-RAS model (ref. 11). For cases involving bends, confluences, constrictions and flow obstructions, more sophisticated hydraulic modeling is generally appropriate, such as a two-dimensional model which can evaluate time-dependent flow conditions or complex geometry (ref. 10).
Design velocity is often determined using the Manning Equation for steady uniform flow as follows (ref. 13):
An iterative process is used to determine the flow depth, yo, because both the area and hydraulic radius are functions of yo. Cross-sectional averaged velocity of flow is then defined as V = Q/A. As noted previously, complex hydraulic systems require sophisticated modeling to determine averaged velocity.
The cross-sectional averaged bed shear stress and cross sectional averaged velocity should be determined by a design professional familiar with hydraulic design practices.
ACB Revetment Considerations
Historically, manufacturers of ACB systems published performance data from full-scale tests performed in accordance with Federal Highway Administration guidelines (ref. 8). Two relatively new ASTM standards have been developed based on the FHWA method: Standard Guide for Analysis and Interpretation of Test Data for Articulating Concrete Block (ACB) Revetment Systems in Open Channel Flow, ASTM D7276 (ref. 3) and Standard Test Method for Performance Testing of Articulating Concrete Block (ACB) Revetment Systems for Hydraulic Stability in Open Channel Flow, ASTM D7277 (ref. 4), that eventually will replace the FHWA test method. This data provides the critical shear stress, τc, and is based on specific flow conditions and ACB system characteristics. The manufacturer should specify whether the critical shear stress is for a unit on a horizontal surface or on an inclined surface. Values for a unit on a horizontal surface are commonly specified. It is important that the designer consider the full-scale test configuration and hydraulic conditions used to derive the critical shear stress on a horizontal surface.
Testing involves the construction of a full-scale test embankment that is subsequently exposed to hydraulic load until failure—defined as the local loss of intimate contact between the ACB unit and the subgrade it protects. A schematic of a typical flume is illustrated in Figure 5. ACB system stability is evaluated by summing the driving and resisting moments about the toe of an individual ACB unit. The inter-block restraint, FR, is ignored, as is any contribution from cables, anchorages and vegetation (see Figure 2).
ACB placement or subgrade irregularities can result in one unit protruding above the ACB matrix, as shown in Figure 3. The protrusion height, ΔZ, is a function of installation practice and block-to-block interface, and is often assumed to be ¼ to ½ in. (6 to 13 mm). However, the designer must consider site-specific conditions and adjust ΔZ as required. The lift force, F’L, resulting from the protrusion is conservatively assumed equal to the drag force, F’D.
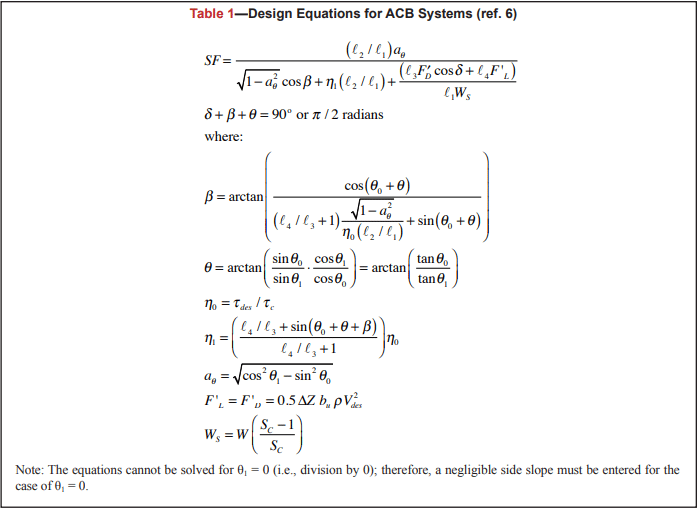
The established design methodology assumed that the flow was parallel to the block and calculated the drag forces using the block width perpendicular to the flow, b (see equation for F’D in Table 1 and Figure 6b). However, in the field not all ACB applications have the flow aligned with the sides of the block. To account for that uncertainty, it is recommended that the diagonal distance of the block, 2l2, be used instead of b in the drag force calculations (see Figure 6b). It is recommended that the designer analyze the project conditions and determine the appropriate dimension for determining the drag forces, F’D, and safety factors on each project. Examples of non-parallel flow conditions are open channels and levees where the flow alignment is uncertain during the life of the project.
The factor of safety against loss of intimate contact is considered to be a function of design bed shear stress, critical shear stress, channel geometry and ACB unit geometry and weight. Figure 2 illustrates unit moment arms based on unit geometry. The safety factor for a single ACB unit is determined from the ratio of restraining moments to overturning moments. Considering the submerged unit weight, WS, unit moment arms and drag and lift forces, the safety factor, SF is defined as (ref. 6):
Dividing by l1WS and substituting terms, the equation for SF resolves to that presented in Table 1. Table 1 also outlines the calculations necessary for determining factor of safety.
DESIGN EXAMPLE
A trapezoidal channel section with 3H:1V side slopes (Z = 3, θ1 = 18.4°) and a base width b of 15 ft (4.6 m) requires stabilization. The 100-year design discharge is 450 ft³/s (12.7 m³/s), and the channel slope So is 0.03 ft/ft (0.03 m/m) (θ0 = 1.72°). The channel has a uniform bed and no flow obstructions (i.e. confluences, bends or changes in geometry). Manning’s n is specified as 0.035. Based on design conditions, the energy grade line Sf is assumed equal to the channel slope So.
Step 1 Determine flow depth and cross-sectional averaged velocity:
R = A/P, hydraulic radius
By iteration, the flow depth yo is determined to be 2.1 ft (0.6 m).
Step 2 Calculate design shear stress:
Step 3 Select target factor of safety:
Based on the analysis of the project conditions, such as type of application, low consequence of failure and the empirical hydraulic model, the designer has recommended a target factor of safety, SFT, for the project of 2.34.
Step 4 Select potential ACB product and obtain geomorphic and critical shear stress data:
The proposed ACB manufacturer specifies a critical shear stress, τc, for the unit on a horizontal surface of 30 psf (1.4 kPa) for a maximum velocity of 20 ft/s (6.1 m/s), submerged unit weight of 38 lb (17.2 kg) and dimensions of 15 (w) x 18 (l) x 5 (h) in. (381 x 457 x 127 mm).
Step 5 Calculate factor of safety against incipient unit movement:
Given;
Ws = 35 lb (16 kg)
bu = 1.5 ft (460 mm)
τc = 30 psf (1.4 kPa)
ηo = 2.96/30 = 0.0987
and determining the following geometrically (see Figure 6);
and assuming (see discussion);
ΔZ = 0.0417 ft (13 mm)
the following are calculated using the equations in Table 1:
For this open channel application the flow is not considered to align with the block, so b = 2l2
aθ = 0.948
θ = 5.16°
β = 19.4°
η1 = 0.08
δ = 65.4°
SF = 2.43
Because the calculated factor of safety exceeds the target, the proposed ACB system is stable against loss of intimate contact.
An ACB Design Spreadsheet (ref. 15) that makes these calculations much easier is available free on request via the CMHA web site.
NOTATIONS:
A = cross-sectional flow area, ft² (m²)
aq = projection of Ws into subgrade beneath block (Table 1)
b = width of channel base, ft (mm)
bu = width of ACB unit in the direction of flow, ft (mm)
FD = drag force, lb (kN)
F’D = additional drag forces, lb (kN)
FL = lift force, lb (kN)
F’L = additional lift forces, lb (kN) (Table 1)
FR = inter-block restraint, lb (kN)
lx = block moment arms, ft (mm)
n = Manning’s roughness coefficient
Q = design discharge, ft³/s (m³/s)
R = hydraulic radius (A/wetted perimeter), ft (m)
SC = specific gravity of concrete (assume 2.1)
Sf = energy grade line, ft/ft (m/m)
So = bed slope, ft/ft (m/m)
SF = calculated factor of safety (Table 1)
SFT = target factor of safety
V = cross-sectional averaged flow velocity, ft/s (m/s)
W = weight of block, lb (kg)
Ws = submerged weight of block, lb (kg) (Table 1)
Ws1 = gravity force parallel to slope, lb (kN)
Ws2 = gravity force normal to slope, lb (kN)
yo = flow depth, ft (m)
Z = horizontal to vertical ratio of channel side slope
β = angle of block projection from downward direction, once in motion, degrees or radians
γ = unit weight of water, 62.4 pcf (1,000 kg/m³)
ΔZ = height of block protrusion above ACB matrix, ft (mm)
δ = angle between drag force and block motion, degrees or radians
ηo = stability number for a horizontal surface (Table 1)
η1 = stability number for a sloped surface (Table 1)
θ = angle between side slope projection of WS and the vertical, degrees or radians (Table 1)
θ0 = channel bed slope, degrees or radians
θ1 = channel side slope, degrees or radians
ρ = mass density of water, 1.94 slugs/ft³ (1,000 kg/m³)
τc = critical shear stress for block on a horizontal surface, lb/ft² (kPa)
τdes = design shear stress, lb/ft² (kPa)
τo = cross-section averaged bed shear stress, lb/ft² (kPa)
REFERENCES
- Standard Specification for Materials and Manufacture of Articulating Concrete Block (ACB) Revetment Systems, ASTM D6684-04(2010). ASTM International, 2010.
- Standard Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Concrete Masonry Units and Related Units, ASTM C140-09. ASTM International, 2010.
- Standard Guide for Analysis and Interpretation of Test Data for Articulating Concrete Block (ACB) Revetment Systems in Open Channel Flow, ASTM D7276-08. ASTM International, 2010.
- Standard Test Method for Performance Testing of Articulating Concrete Block (ACB) Revetment Systems for Hydraulic Stability in Open Channel Flow, ASTM D7277-08. ASTM International, 2010
- Design Manual for Articulating Concrete Block Systems. Harris County Flood Control District, Houston, Texas, 2001.
- Design Manual for Articulating Concrete Block, ACBMAN-001-20. Concrete Masonry & Hardscapes Association, 2020.
- Bridge Scour and Stream Instability Countermeasures: Experience, Selection, and Design Guidance – 3rd Edition. Federal Highway Administration Hydraulic Engineering Circular No. 23.
- Clopper, P. E. and Y. Chen. Minimizing Embankment Damage During Overtopping Flow, Technical Report FHWA RD-88-181. Federal Highway Administration, 1988.
- Clopper, P. E. Hydraulic Stability of Articulated Concrete Block Revetment Systems During Overtopping Flow, Technical Report FHWA RD-89-199. Federal Highway Administration, 1989.
- RMA2 Version 4.5. United States Army Corps of Engineers. USACE Waterways Experiment Station, 2008.
- HEC-RAS Version 4.1. United States Army Corps of Engineers. USACE Hydrologic Engineering Center, 2010.
- Articulated Concrete Block for Erosion Control, ACBTEC-001-14, Concrete Masonry & Hardscapes Association, Herndon, Virginia, 2014.
- Morris, H. M. and J. Wiggert. Applied Hydraulics in Engineering, Second Edition, James Wiley & Sons, 1972.
- Lipscomb, C.M, C.I. Thornton, S.R. Abt, and J. R. Leech. Performance of Articulated Concrete Blocks in Vegetated and Un-Vegetated Conditions. Proceedings of the International Erosion Control Association 32nd Annual Conference and Exposition, Las Vegas, NV, February 5-8, 2001.
- Articulating Concrete Block (ACB) Design Spreadsheet, ACB-XLS-001-19. Concrete Masonry & Hardscapes Association, Herndon, Virginia, 2019.